Poison Ivy Rash
Understanding Poison Ivy Rash
Poison ivy rash is an allergic reaction to urushiol, an oily resin found in poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac plants. The rash appears as red, itchy, and blistering skin within 12 to 48 hours after contact with the plant. It can affect any part of the body that comes into contact with the oil, and the rash can spread if the oil remains on the skin, clothes, or other surfaces.
While poison ivy rash usually resolves on its own within 1 to 3 weeks, severe cases may require medical treatment. Over-the-counter creams and antihistamines can help relieve mild symptoms, while prescription medications might be necessary for more severe reactions.
Effective Treatment for Poison Ivy Rash at Riva Dermatology
At Riva Dermatology, we offer treatments to help relieve the symptoms of poison ivy rash and prevent secondary infections. Our dermatologists provide personalized care to ensure a quick recovery.
Examples of Poison Ivy Rash
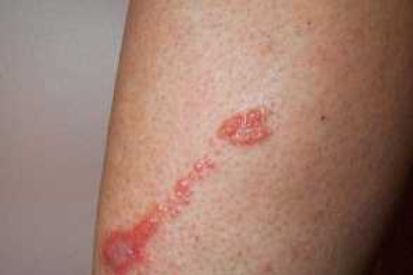

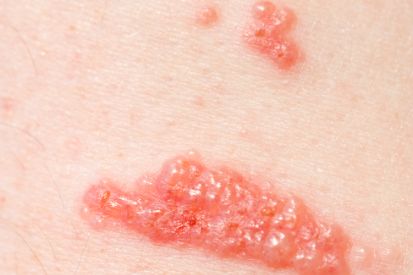
Symptoms of Poison Ivy
- Poison ivy rash symptoms usually appear quickly – about 12 to 48 hours after contact.
- Symptoms may last for two to three weeks and almost always require some form of treatment.
- Typical symptoms of poison ivy rash include redness, itching, swelling, and blisters.
What Causes Poison Ivy?
- The rash of "poison ivy" occurs when the skin comes in contact with the leaves, stems or roots of poison ivy, poison oak or poison sumac.
How to Prevent Poison Ivy Rash
To prevent a poison ivy rash, learn to identify the plant with its distinctive three-leaf pattern. When in areas where poison ivy may be present, wear protective clothing such as long sleeves, pants, closed shoes, and gloves
Poison Ivy Rash FAQs
Poison ivy rash is caused by an allergic reaction to urushiol, an oily resin found in poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac plants.
Symptoms typically appear within 12 to 48 hours after contact with the plant and include red, itchy, and blistering skin.
Treatment includes washing the skin thoroughly, applying over-the-counter creams and lotions, taking antihistamines, and using prescription medications for severe cases.
The rash itself is not contagious, but the oil can spread if it remains on the skin, clothing, or other surfaces. Washing thoroughly can help prevent spreading.
Avoiding contact with the plants, wearing protective clothing, and using barrier creams can help prevent poison ivy rash. Learning to identify the plants is also essential.
Seek medical attention if the rash is widespread, severe, or accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling, or signs of infection such as pus or fever.
Poison Ivy Treatments
- Topical Steroids: Prescription or over-the-counter topical corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation, redness, and itching associated with a poison ivy rash.
- Oral Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine, can help relieve itching and discomfort.
- Calamine Lotion: Applying calamine lotion to the affected areas can help soothe the skin and reduce itching.
- Prescription Medications: In severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe stronger medications, such as oral steroids, to manage widespread or persistent symptoms.
Featured Products
Check your local office for current stock!
Check your local office for current stock!


